GCash Pera Outlets are official GCash-affiliated stores that offer GCash services. This post explains how you can apply as one.
GCash has certainly utilized different ways to leverage technology to make payments and money movements easier for everyone. Setting up your own Pera Outlet is one of these. Now you don’t even need to go outside to set up your new account. You just need your GCash app to start.
This definitely lowers the bar for stores that want to opt in, as all of the requirements are coursed through the app, without needing to spend some time going to a physical office to register.
What is a GCash Pera Outlet?
Basically, this means as a merchant you are officially becoming GCash-accredited for all supported transactions. Actually, some sari-sari stores do this already but with the use of the owner’s personal GCash account. Some are even savvy enough to use their personal QR codes to collect payment.
However, having official accreditation means more protection for GCash users and more earnings for sari-sari stores. This is because official Pera Outlets don’t charge extra fees, and merchants would also be able to earn commissions from certain transactions coursed through them. Additionally, it can enable merchants to provide value-added services that only Pera Outlets can do (ex., GCash Padala).
What benefits would I get if I set up my own Pera Outlet?
- You get 0.5% of any cash-in, cash-out, and padala transaction.
- You get Php 3 per biller transaction that goes through your account.
- You get free signage kits from GCash.
- You get to be officially listed in the main GCash Padala providers as free marketing.
- You get a separate merchant wallet with a Php 500k limit.
Unfortunately, the services listed above are the only ones currently with commissions.
What services can I provide as a GCash Pera Outlet?
Currently here is the list of services you can provide:
- Cash In
- Cash Out
- Padala
- Pay Bills
- Buy Load
- Pay QR
Eventually, as more merchants come on board, more features may become available.
What’s the difference between GCash Pera Outlets and GCash Payments acceptance?
Any store or SME or entrepreneur can accept GCash payments (online and QR) as a mode of payment.
GCash Pera Outlets are for existing stores providing GCash services to users. Usually, it is the sari-sari stores that become GCash Pera Outlets. If you are a GCash Pera Outlet, you can also accept GCash QR Payments.
How do I become a GCash Pera Outlet?
Everything you need is right in the GCash app, go to GLife and search for GCash PO. Once inside, you can then apply your store as a Pera Outlet.
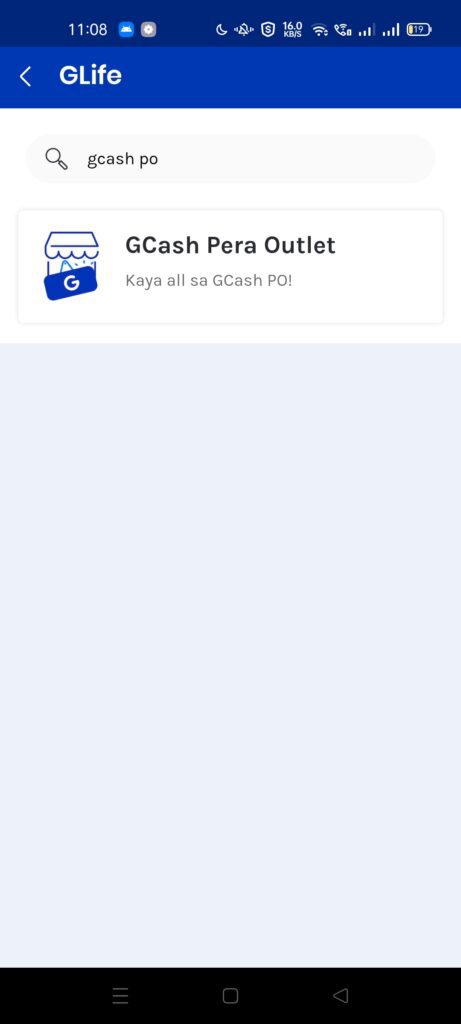
What are the requirements I need?
First, you need to have a storefront, meaning you should own a store so that customers can transact with you publicly. Sari-sari stores comprise the majority of GCash Pera Outlets out there. But it does not mean that you need to be a sari-sari store to be accepted.
Another requirement is a separate phone for Pera Outlet transactions. I would suggest you as the owner do the actual GCash PO application itself in a separate GCash account. Creating multiple accounts is easy, but you will still need to undergo verification for the new account.
For GCash verification and for receiving GCash Padala, you would need a valid ID from this list:
- UMID
- Driver’s License
- SSS ID
- Passport
- Phil Postal ID
- PRC ID
- Pag-IBIG ID
- Philsys / ePhilID
- Alien Certificate of Registration (ACR) – if you are a foreign national
- Student ID, Birth Certificate – if you are a minor, and applying for GCash JR
If you don’t have an ID from this list, you need to file a Help Support ticket to help in your verification.
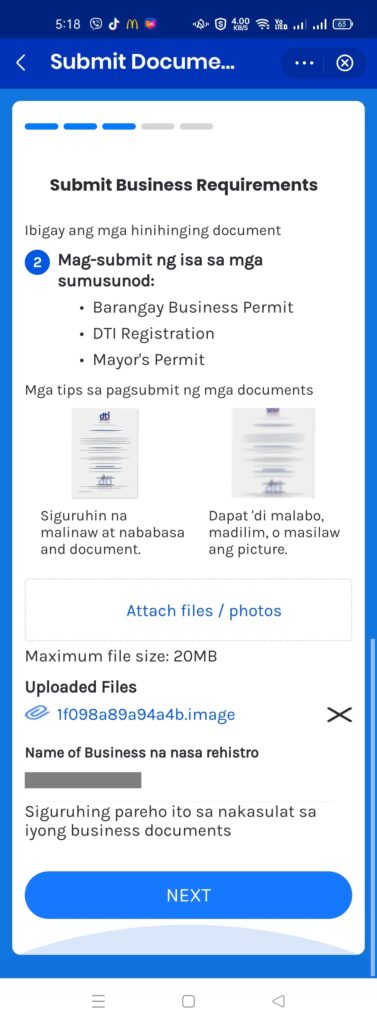
As for the GCash PO application itself, you would need to take pictures of:
- Barangay Business Permit
- DTI Registration
- Mayor’s Permit
- A picture of your storefront including you as the owner
- A selfie
Lastly, you would also need to build up your Anti Money Laundering Act (AMLA) knowledge as there will be an exam. There will be a training video to watch before that, fortunately.
How do I start my application?
Here are the steps for registering as a GCash Pera Outlet:
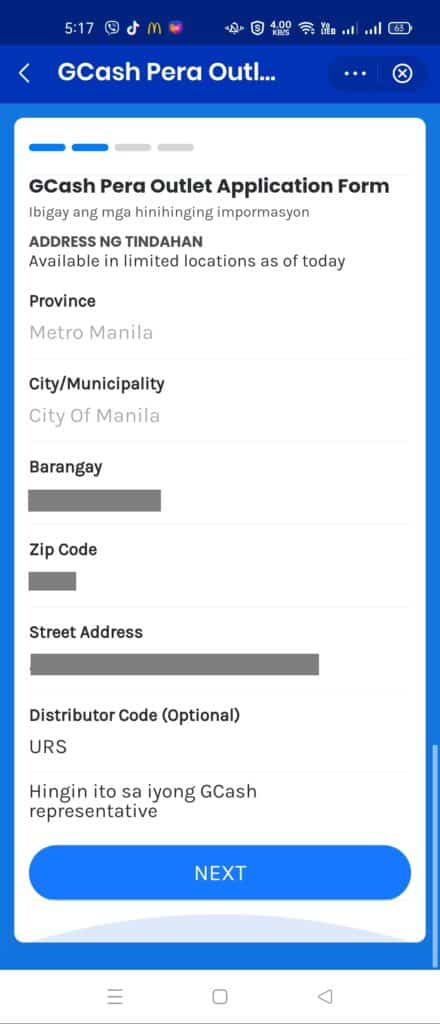
- From the GCash PO Apply page, start an application.
- On the succeeding pages, input the details required in the form, as well as upload the needed photos. Once the application is filed, there is a lead time of 3-5 days of review before you are approved or rejected.
- There should be a selection from the GCash PO main page to take the Anti Money Laundering (AML) Module.
- Input the requirements, watch the Anti Money Laundering Act (AMLA) video and take a short exam to finish the application. Don’t worry if you get the AMLA exam wrong, you can take it as many times as you like. The passing rate is 11/15 correct answers.
Registration screenshots:


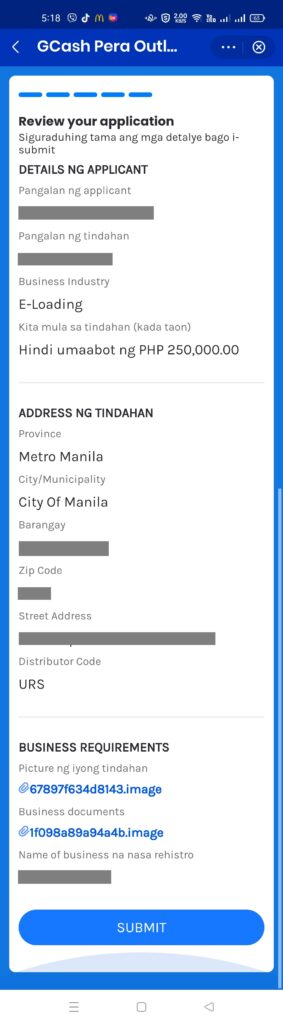

AML Module screenshots:

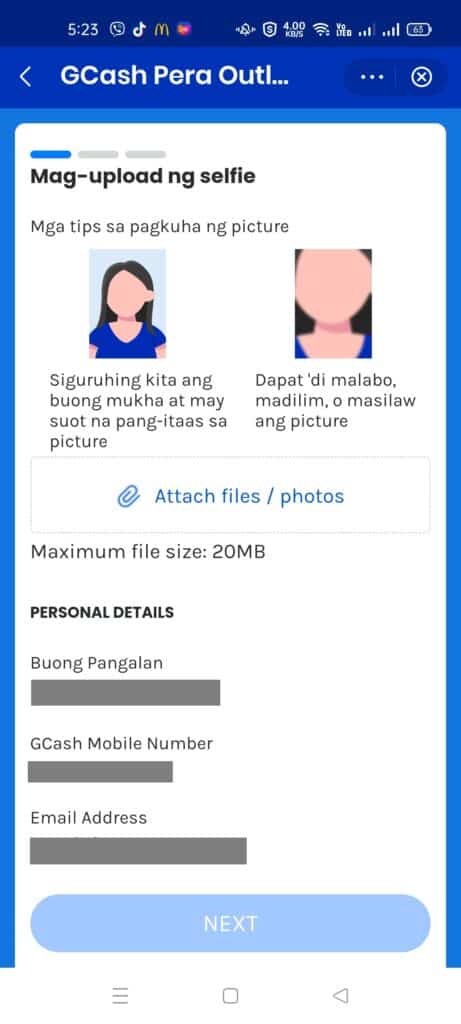

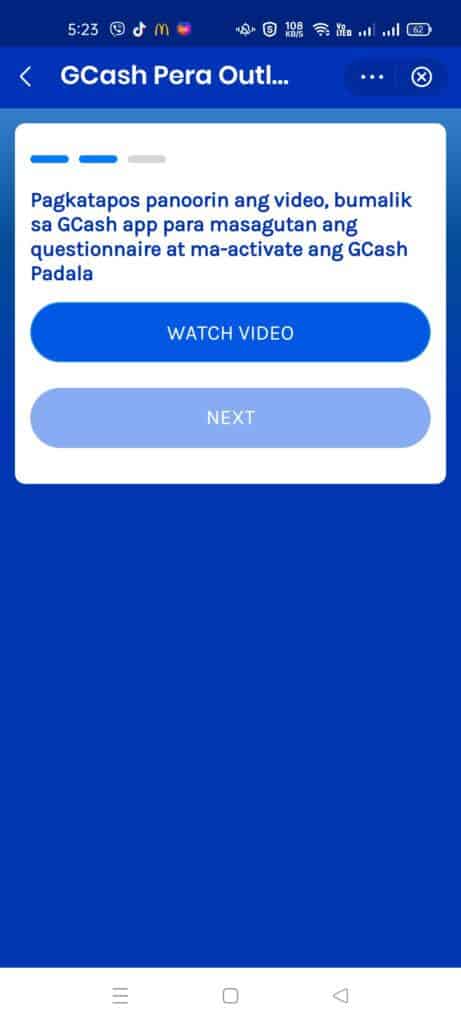

Why do we need to do Anti Money Laundering Act (AMLA) testing?
This is a requirement of the BSP for any entity that handles funds like GCash as they have the mandate to stop money laundering and terrorist financing.
As GCash Pera Outlets are the front liners in accepting and releasing funds to many people, it is vital for everyone to be at least knowledgeable on AMLA and report suspicious fund transfers.
What are the notable points of AMLA to help me answer the exam?
Here is the actual law if you want to read the whole thing. But I’ve also condensed it into a summary for easier reading below:
- The AMLA, or The Anti-Money Laundering Act of 2001 is also known as Republic Act No. 9160.
- Money Laundering is a crime where “dirty money” or money used in illegal activities is used in transactions to make them appear legitimate.
- Some direct penalties include:
- 7-14 years imprisonment (and a fine of more than Php 3M) for the act of transacting using dirty money itself
- 4-7 years imprisonment (and a fine of Php 1.5 – Php 3M) for enabling the transaction of dirty money
- 6 months to 4 years imprisonment (and a fine of Php 100k – Php 500k) for failing to report transactions of dirty money
- Unlawful Activities are crimes that generate dirty money. The list includes:
- Kidnapping for ransom
- Drug trafficking and related offenses
- Graft and corrupt practices
- Plunder
- Robbery and Extortion
- Jueteng and Masiao
- Piracy
- Qualified theft
- Swindling
- Smuggling
- Violations under the Electronic Commerce Act of 2000
- Hijacking; destructive arson; and murder, including those perpetrated by terrorists against non-combatant persons and similar targets
- Fraudulent practices and other violations under the Securities Regulation Code of 2000
- Felonies or offenses of a similar nature that are punishable under the penal laws of other countries
- Terrorism financing and organizing or directing others to commit terrorism financing (R.A. 10168)
- Attempt/conspiracy to commit terrorism financing and organizing or directing others to commit terrorism financing (R.A. 10168)
- Attempt/conspiracy to commit dealing with property or funds of a designated person
- Accomplice to terrorism financing or conspiracy to commit terrorism financing
- Accessory to terrorism financing
- The AMLC (Anti Money Laundering Council) consists of:
- The governor of the BSP as chairman
- The commissioner of the Insurance Commission
- The chairman of the SEC
- Covered transactions are transactions that amount to Php 500k in one given day.
- Suspicious transactions are transactions, regardless of the amount that has these circumstances:
- There is no economic justification.
- The client is not properly identified.
- The amount does not match the financial capacity of the client.
- The transaction seems to avoid being subjected to reporting requirements.
- The transaction seems to deviate from what the client normally does with past transactions.
- The transaction is connected to an unlawful activity.
- Any transaction that is similar to what was mentioned above
- Covered institutions are mandated by the AMLA to submit reports of covered and suspicious transactions to the AMLC. These are:
- Banks supervised by BSP
- Insurance companies regulated by the Insurance Commission
- Dealers of securities that are supervised by the SEC
- Any reports to the AMLC should be confidential, otherwise, the penalty is 3-8 years and has a fine of Php 500k – Php 1M.
- Records of transactions should be saved for 5 years. Penalties if not followed include 6 months – 1-year imprisonment and a fine of Php 100k – Php 500k.
- False or malicious reporting also has a penalty of 6 months – 1-year imprisonment and a fine of Php 100k – Php 500k.
- The AMLC can file a freeze order with the Court of Appeals for any funds that may be connected to unlawful activities. The freeze order is good for 20 days until extended.
- The AMLC can examine any bank deposit or investment if there is probable cause that violates the AMLA.
What do the free banners and guides look like?
After applying for GCash PO status and getting approved, we were visited by the local distributor with free banners and guides. We now post these in front of our store.



Summary
I’ve talked about how to apply for becoming a GCash Pera Outlet. This allows you to earn extra from helping customers with their GCash transactions. The main requirement is you need to have a store and you also need the permits you acquired in running that store. You also need to pass a small Anti-Money Laundering Act (AMLA) related exam.
Applications are easy as you can do that from within the app, via GLife and GCash PO.
After reading about what GCash is, here are the main GCash features:
Fund Transfers:
Cashing In/Out:
Payments:
New Services:

Paano update gcash
Sa Google Play po puwedeng imanual update siya
Interesting. Thank you.
Sana mag pede na sa IOS phone ang gcash PO..🙏🙏
Unfortunately android only lang siya
Im interested
Thank you…
Pano po pagwala pang business permit ang store?.
Kailangang kumpleto para maging GCash PO. Hindi ba puwedeng kumuha?
Hi, kailangan po bang my pundo ang applicant? Magkano po minimum?
Puwede na magpondo ang applicant sa loob mismo ng GCash PO. Hiwalay ang wallet ng user sa GCash PO wallet.
If foreigner can apply?
Puwede as long as kumpleto requirements
Pwede ba name ko i register sa G cash Pera Outlet pero yung business permit ng sari sari nakapangalan sister ko?
Yes puwede