Learn how to buy and sell crypto assets in PDAX using GCash.
Disclaimer: This post aims to educate and not to give financial advice. Investments have different risks, and it is up to the investor to do due diligence and make decisions regarding his money.
As we see mainstream adoption of Bitcoin as legal tender (like in El Salvador) more and more, it becomes more important to have at least a small investment in cryptocurrencies. Here in the Philippines, we have a laissez-faire policy with cryptocurrencies. Our BSP is more often than not stricter with money laundering rules with this but otherwise tends to treat it as a security.
I’ve talked about how to buy cryptocurrencies before, in Coins.ph and in Binance, but here is another channel we can tap on — Philippine Digital Asset Exchange or PDAX.
In the Philippines, PDAX as an exchange has more supported coins now than in Coins.ph and is quietly surpassing it in terms of adoption. The additional coins recently supported are LINK, BAT, AAVE, UNI, GRT, COMP, and ENJ. If you want to learn about these coins, you can use Coinmarketcap to read about them.
PDAX as an exchange had its growing pains earlier this year when a trading glitch caused it to lock all of the users’ funds. However, it has since owned up to it and has promised more transparency and capability moving forward.
What are some advantages of PDAX over Coins.ph?
PDAX is an exchange, unlike Coins.ph which has both an exchange and a wallet with its ecosystem. With it being an exchange, users can focus on trading and investing in cryptocurrencies.
Also, PDAX has more flexibility as an exchange, since it also has stable coins like Tether and USDC. These stablecoins enable you more flexibility as you can convert easily from any cryptocurrency to this, and also allows you to leverage De-Fi (decentralized finance) as a lot of products (especially decentralized exchanges) use stablecoins in their liquidity pools.
How to buy cryptocurrencies using GCash
PDAX has a lot of cash-in options available, but it has partnered with Paymongo for GCash acceptance.
Here are the steps in the PDAX app:
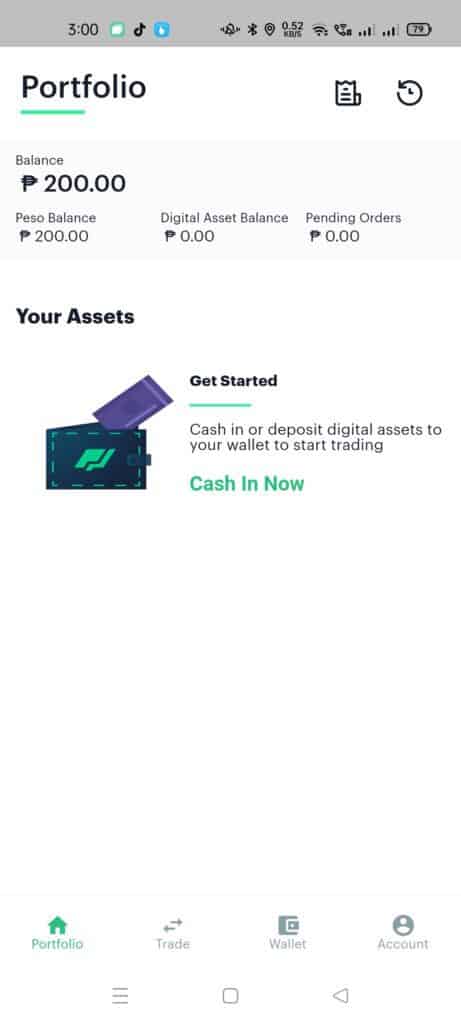
- From the main page of the app, click on the Wallet button below.
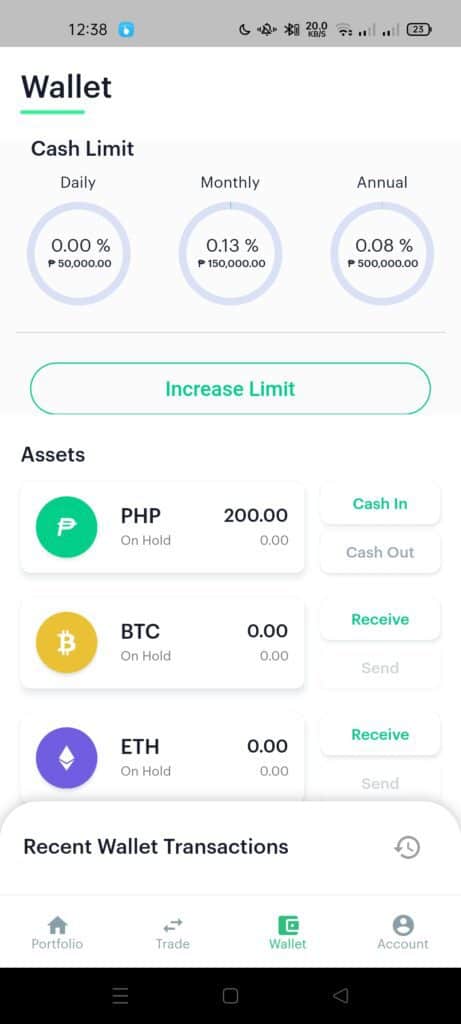
- From the Wallet page, select the “Cash In” button beside the PHP asset box, and you will go to the Cash In page.
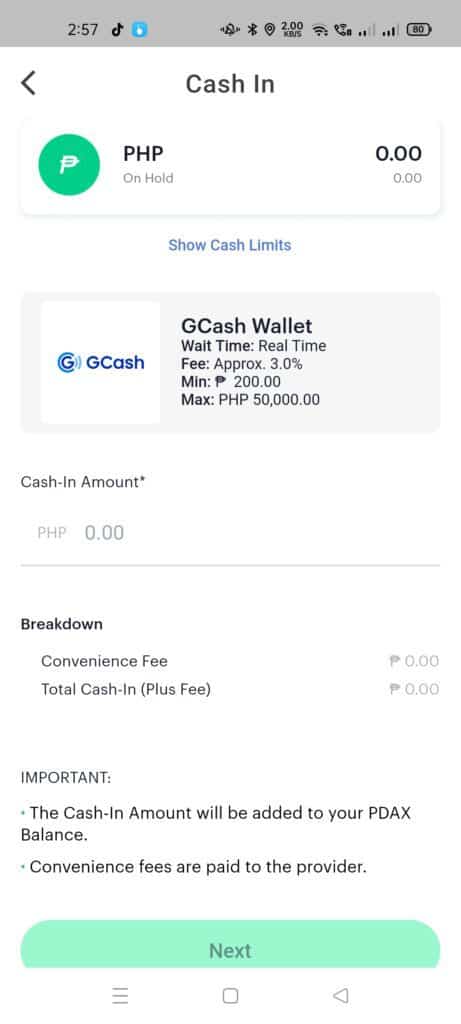
- From the Cash In page, click on the E-Wallet tab and select GCash Wallet.
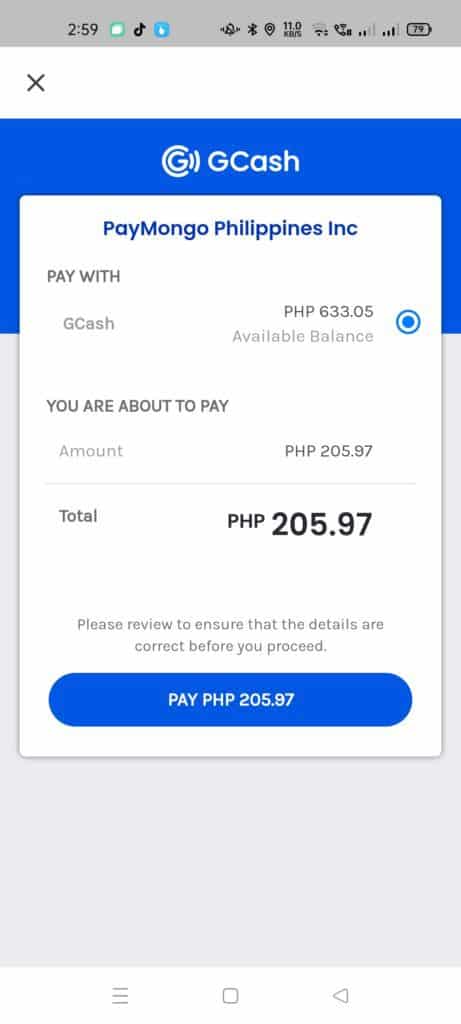
- In the GCash Cash In page, input the amount and click next. Take note that there is a convenience fee and this fee is included on top of what you need to pay.
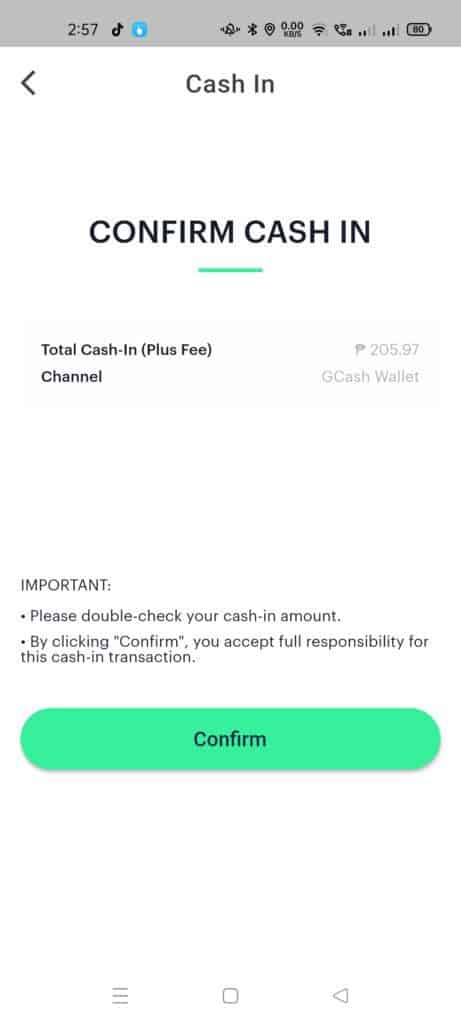
- Confirm the Cash In to initiate the GCash online payment.
- You will need to authenticate yourself using your GCash credentials as well as to input the one-time password. After authentication, you can confirm the payment on the GCash side.
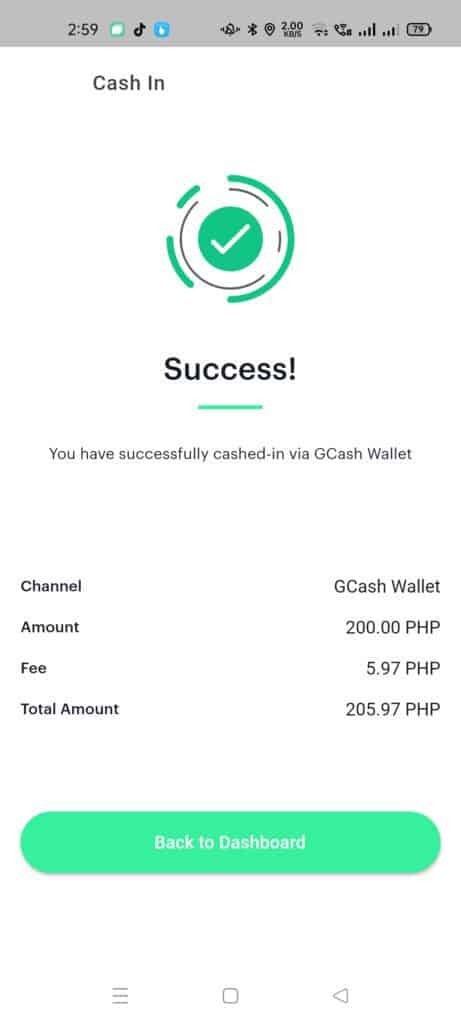
- After payment, your new balance will reflect on the Portfolio page.

GCrypto/PDAX supported crypto assets
To explain in a nutshell, the difference between “coin” and “token” is that coins are the main units of information in a blockchain. Any transaction or information is tracked by coins. Tokens, on the other hand, are real-world applications that are used on top of a blockchain, and they are supported by the coins in that chain.
Tokens are created so that projects don’t need to build a new blockchain from scratch to keep track of transactions and information. They can just ride on existing blockchains.
In the table below, if the crypto asset has the same name as the blockchain, it is a coin of that blockchain. Otherwise, it’s a token.
| Crypto Asset | Blockchain | Short Description |
|---|---|---|
| Ethereum (ETH) | Ethereum | The pioneer for blockchains that run smart contracts; a lot of tokens use this as the backbone of their decentralized apps (dApps) |
| Bitcoin (BTC) | Bitcoin | The pioneer for all crypto assets; its coin is used mainly as a store of value (like virtual gold) and is the most well-known and mainstream asset |
| Solana (SOL) | Solana | An alternative to Ethereum and is known for very high-speed transactions |
| Avalanche (AVAX) | Avalanche | An alternative to Ethereum and is known for speed and security; also has dApps in its blockchain |
| USD Coin (USDC) | Ethereum | A mainstream USD stablecoin token in Ethereum; USD stablecoins peg their value to the US Dollar |
| Tether (USDT) | Ethereum | The biggest USD stablecoin token by market value; hosted in Ethereum |
| Binance Coin (BNB) | BNB | A coin that is tied with Binance, the largest centralized cryptocurrency exchange; also known for its speed and also has dApps in its blockchain |
| Cardano (ADA) | Cardano | An alternative to Ethereum and seeks to improve on Ethereum’s issues |
| Polkadot (DOT) | Polkadot | A blockchain that allows other blockchains to talk with each other |
| Litecoin (LTC) | Litecoin | An original fork (“copy that diverged from”) of Bitcoin, and is generally cheaper and faster than Bitcoin |
| Uniswap (UNI) | Ethereum | A decentralized finance (de-fi) platform mainly used as an exchange; you can “swap” tokens with other tokens in the ETH blockchain |
| Polygon (MATIC) | Ethereum | A scaling solution to ETH, which allows the creation of sidechains to make transactions in ETH cheaper and faster |
| Chainlink (LINK) | Ethereum | Implements oracles, or systems that track data outside of the blockchain; examples are financial data, sports data, etc |
| Stellar (XLM) | Stellar | A blockchain that is known for very, very low fees and is good for micropayments |
| Bitcoin Cash (BCH) | Bitcoin Cash | A fork of Bitcoin itself when there was a disagreement about handling how transactions were validated; still works mostly similarly to Bitcoin but is not as popular |
| Axie Infinity (AXS) | Ronin | The Ronin sidechain is built on top of ETH to easily support the Axie Infinity game |
| AAVE | Ethereum | This is a de-fi platform for lending and borrowing assets in the ETH platform |
| The Graph (GRT) | Ethereum | Allows to get data across multiple projects in the ETH blockchain and makes them available easily |
| Basic Attention Token (BAT) | Ethereum | Aims to democratize attention sharing and distribute advertising money efficiently across readers and publishers |
| Enjin (ENJ) | Ethereum | Makes management of virtual goods easier; known for making non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and game-related goods and collectibles |
| Sushiswap (SUSHI) | Ethereum | Another popular decentralized exchange; this fork of Uniswap has different features from its parent |
| Smooth Love Potion (SLP) | Ronin | The in-game currency of the Axie Infinity game; allows you to breed Axies which is a core part of the game itself |
Other Questions
How much is the convenience fee?
The fee is 3% of the total amount and is added on top of the actual cash-in amount.
Does PDAX also support GCash cash out?
Currently no.
What’s the cheapest way to buy in PDAX and get the money instantly?
The no-fee ones usually mean that the cash-in is not going to happen on the same day. But if you want real-time transfer and you also have a GrabPay account, you can go through that channel as it has the lowest fixed fee of Php 25.
You just need to transfer from your GCash wallet to your GrabPay first via Bank Transfer. Take note though that since bank transfers use Instapay, there’s a fee of Php 15 when you use GCash. If you add the PDAX cash-in fee of Php 25, then the total fee should be Php40.
I recommend you choose this route if this fee is cheaper than the 3% you would have spent cashing in using direct GCash (i.e., Php 40 / 0.03 = Php 1,333). In short, you should go with GrabPay if you are planning to cash in more than Php 1333 pesos.
Do I need to go through validation from PDAX?
No, you won’t need to validate, other than increasing your limits
Summary
We talked about how we can cash-in in on PDAX via GCash. Cash-in is in the form of Paymongo payments. PDAX as an exchange has more cryptocurrencies than any other in the Philippines.
If you do plan to cash in, always take note of the fees.
If you are also interested in other cryptocurrency or investment-related posts, here are some:
After reading about what GCash is, here are the main GCash features:
Fund Transfers:
Cashing In/Out:
Payments:
New Services:
